Supply Chain Management
Importance and Mission
The oil and gas industry operates in just about every imaginable geographic and climatic conditions across the world. Managing complex supply chain is a success factor to ensure effective management of the flow of product or service including on-time delivery of people, materials and equipment to operational sites. In addition, to support PTTEP Net Zero 2050 target.
Supply Chain Management will not only contain possible risks on the operations and corporate reputation but also increase operational efficiency, transparency, and shared values between PTTEP and suppliers. Such management as guided by the principles of cost-effectiveness, transparency, efficiency, effectiveness, and traceability involves the first step in selecting vendors and suppliers. It entails a review on suppliers' management of ESG (environment, social and governance) risk, relationship building, and suppliers' capability enhancement through the adoption of digital technology.
Goals
1. Zero Incident Organization
PTTEP is committed to Safety, Security, Health and Environment (SSHE) management to achieve zero incident organization target. The goal encompasses major accident events, oil and chemical spillage, motor vehicle incidents, marine vessel incidents, total recordable injury and loss time injury, to ensure nobody gets hurt and everybody returns home safely. More information is available in the SSHE Policy.
2. Green Supply Chain
PTTEP implemented Green Supply Chain in 2019 through the green procurement of goods and services and the development of energy-efficient logistics, in order to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from combustion which causes global warming.
3. Local Content
PTTEP supports local businesses and encourages the procurement of goods and services in the operating areas, to support local economy, employment and income distribution, resulting in PTTEP having a good relationship and gaining acceptance in the countries where PTTEP operates. Moreover, PTTEP encourages suppliers to operate with responsibility and to source products and services in local areas.
4. Supplier Management and Vendor Sustainable Code of Conduct
PTTEP sources goods and services with honesty, integrity and fairness as guided by the Company's governance principles. The Company takes into account environmental impacts; economic and social factors; contract terms and conditions; pricing; quality; delivery; and SSHE requirements. On top of that, contractors must comply with all of the principles and give importance to social responsibility.
PTTEP believes that it is vital to conduct business under Good Corporate Governance and Business Ethics and emphasizes the rights of internal and external stakeholders' rights through the Supply Chain Management Policy and related activities. For example, PTTEP joins the Integrity Pact (IP) to strengthen the national fight against corruption in line with the procurement and anti-corruption laws. PTTEP is also a member of Thailand's Private Sector Collective Action Coalition Against Corruption (CAC).
5. Cost Effectiveness
The Supply Chain Management Policy to source quality goods and services at the best prices and at the best time is consistent with PTTEP's objectives, ethics and policies as well as relevant laws. PTTEP has adopted more digital procurement systems which have further lowered expenses but raised efficiency.
PTTEP also resorts to PTT Group's integrated procurement scheme for selected goods and services, in order to increase leverage and synergy across the petroleum supply chain. Such goods and services are, for instance, air filter for gas turbines, spare part filters, turbine compressor maintenance services, and procurement of life insurance for PTT Group's personnel.
Supply Chain Management Approach
PTTEP's Supply Chain Management Policy focuses on the efficiency in preventing and reducing social and environmental risks and the monitoring of suppliers that may affect stakeholders' trust in PTTEP's operation and consequently affect the overall business. Under the policy, the procurement of local goods and services is encouraged to support the local economy and generate income where PTTEP operates.
PTTEP Supply Chain Management (SCM) model
Below is PTTEP's Supply Chain Management model with illustration of key activities, roles, as well as supply chain management processes to facilitate all petroleum exploration and production activities in an integrated manner.
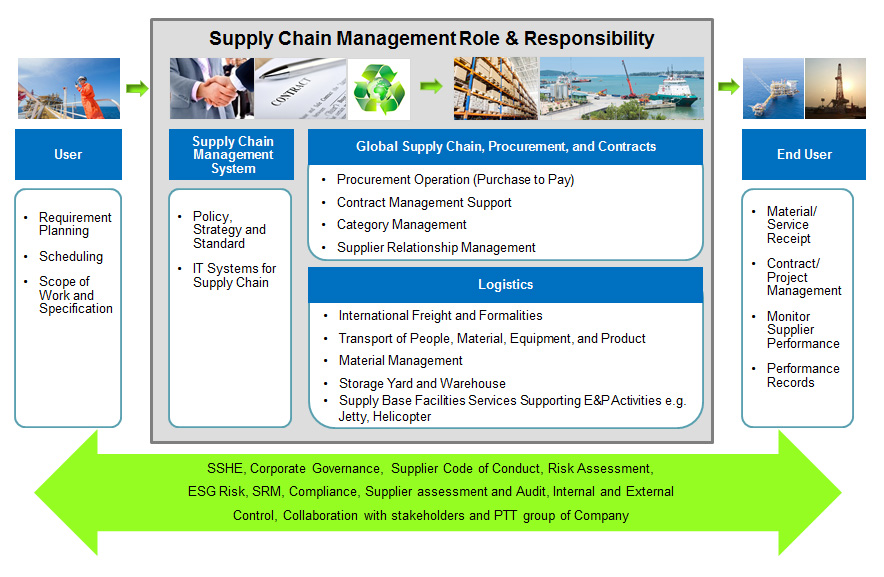
Supply Chain Management principles
PTTEP's Supply Chain Management principles consist of four main elements as follows:
1. Supply Chain Management System
To establish the management system that entails supply chain management policy, standards, operational guideline and the adoption of relevant information technology for all PTTEP operating assets in Thailand and abroad.
2. Supply chain management strategies, Procurement and Contracts
To provide in-depth market intelligence and technical information for analysis and the formulation of strategies for each function and to handle suppliers through the evaluation of new vendors and the management of relationships with critical suppliers. The unit is also responsible for procurement process and contracts for various activities, from sourcing, bidding, negotiation, contract preparation and issuance of orders to contract management support and advice to the Procurement Committee to ensure compliance with contracts as well as efficiency, transparency and accountability.
3. Logistics
To manage the variety of logistics operations; for instance, personnel and cargo transportation, import/export and customs clearance, and waste management, in compliance with the Company's rules and international safety standards for zero environmental impacts. It is also responsible for inventory management, to strike a balance of investment, expenses, and operational continuity.
4. Petroleum Development Support Base
PTTEP operates two supply bases supporting offshore exploration and production activities in the Gulf of Thailand and the Andaman Sea. These bases provide vessel berthing, cargo handling and warehousing services certified by international standards like ISO 14001, ISO 22301, ISO 45001, and ISPS Code, also to other E&P companies operating in Southeast Asia.
Procurement and Contract Strategy
The framework and strategy for procurement and contracts, as shown below, is to align long-term targets with the Company's business objectives and direction. It also guides the procurement unit on the execution of activities, to achieve the targets in a sustainable manner.
PTTEP Procurement and Contract Strategy 2020 - 2024
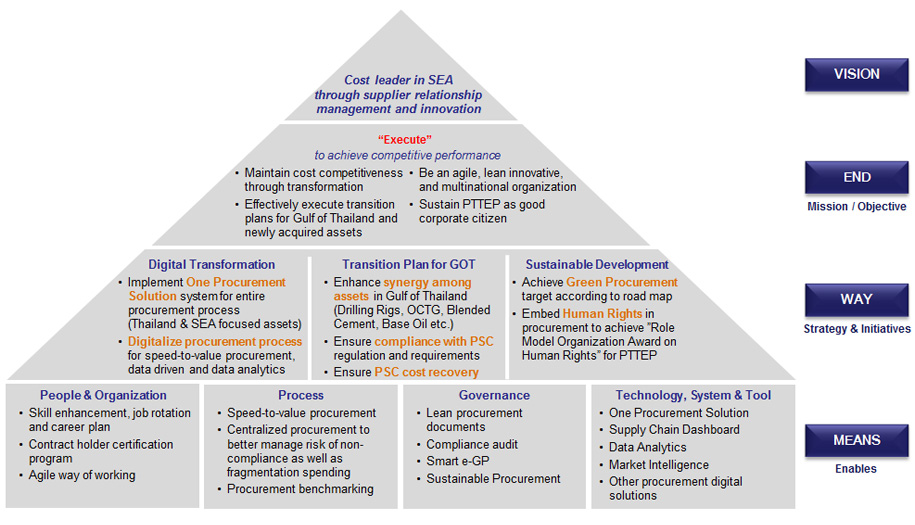
To integrate ESG considerations into supply chain, PTTEP includes clauses in its general procurement terms and conditions for procurement to address business ethics, safety, security, health and the environment to require suppliers and contractors to conduct their business in conformance with the laws and PTTEP's requirements of Safety, Security, Health and Environment Management System (SSHE MS) and the company's business ethics as in alignment with Supplier Code of Conduct and to avoid potential conflicts with ESG requirements. PTTEP's pre-qualification assessment covers ESG aspects to select appropriate suppliers/vendors; it prioritizes the level of enforcement and engagement with suppliers/ vendors. PTTEP has included % (weight) of ESG assessment in the Pre-qualification process. Suppliers who will be participating in any of the project categories for tendering/bidding with the contract value of USD 1 million and above. The company will apply 100% screening and evaluating vendors according to their business categories. The evaluation process is done by a committee consisting of the following sections: 1. Technical and Quality section 2. Safety, Security, Occupational Health and Environmental (SSHE) section 3. Commercial, Legal and Social section. Each section of the committee has the authority to consider and evaluate independently from one another to ensure that the vendor has the qualification to participate in PTTEP's work. This means that if vendors fail one out of three criteria/committee above then, they will not pass the pre-qualification process altogether. As a result, suppliers are excluded from contracting if they cannot achieve minimum ESG requirements within a set of timeframe. The evaluation is based on fairness, equality, and transparency for the highest benefit to PTTEP where suppliers with better ESG performance are preferred by applying a minimum weight to ESG criteria in supplier selection and contract awarding. The implementation of such supplier ESG programs are overseen by Executive Management. The key elements are as follows:
Category Management
In order to ensure the proper management of PTTEP suppliers, the identification of suppliers is conducted to classify the category of each supplier group. The identification of suppliers considers the following criteria
- Spending Volumes,
- Risks (e.g. providing of critical component or non-substitutable supplier)
PTTEP's category management system catalogues goods and services according to abovementioned criteria, and is supported by regular analysis on market condition and internal demand. This measure is expected to deliver maximum efficiency in terms of cost, on time delivery and preferred quality. The three risk aspects including Supply Risk, ESG Risk and Technical Risk are considered in the procurement process for risk assessment, to be in line with PTTEP's policy on sustainable growth
Category Management
PTTEP identifies critical suppliers by conducting work category analysis to classify & prioritize work categories, then select critical suppliers from important and high-priority work categories from their spending volume and risks (e.g. providing of critical component or non-substitutable supplier). PTTEP uses Supplier Positioning Model (SPM) as tools to identify and analyses relationship between "Risk" and "Profit Potential" in which can be described as followed:
1. "Risk" associates with
a. Sustainability (Environmental, Social, Governance - ESG) and technical risk during operation including supplier who provide critical component
Sustainability and Technical Risk that arising during operations. Safety and environmental and reputation impact risks are also taken into consideration apart from technical risks such as financial, design maturity, manufacturing/service complexity, and legal/non-compliance impact. The weight of Sustainability and Technical Risk is accounted for 50% of total risk.
b. Supply risks, non-availability or failure of supplied materials and services.
Supply Risk arising from the vulnerability of the business to the unreliability of the supply market at the acquisition stage of the procurement process. Criteria for consideration include company's experience with product/ service, delivery performance, geographical distance, potential suppliers, non-substitutable supplier, and degree of market saturation. The weight of Supply Risk is accounted for 50% of total risk.
2. "Business Relevance and Profit Potential" is the degree of opportunity, which exists for the procurement process to contribute to Company's profitability. Criteria for consideration to determine the level of Profit Potential include, for example, company's annual spending (high volume spending) and degree of opportunities that reflect in terms of supplier's turnover, potential suppliers, price elasticity, specifications, degree of market saturation.
SPM is divided by 4 categories: Critical, Bottleneck, Leverage and Routine. Critical suppliers are suppliers who have high profit potential (annual spending value above 1 MMUSD) and pose high technical and supply risk and categorized in Critical, Bottleneck, Leverage quadrants of the SPM model. While critical suppliers are suppliers who pose a very high or high risk and were categorized as high-risk tier 1 suppliers, we determine Tier 2 suppliers by extending vision through critical tier 1 suppliers to identify and provide a list of their critical suppliers (Tier 2 to PTTEP where products /services direct or indirect to PTTEP).
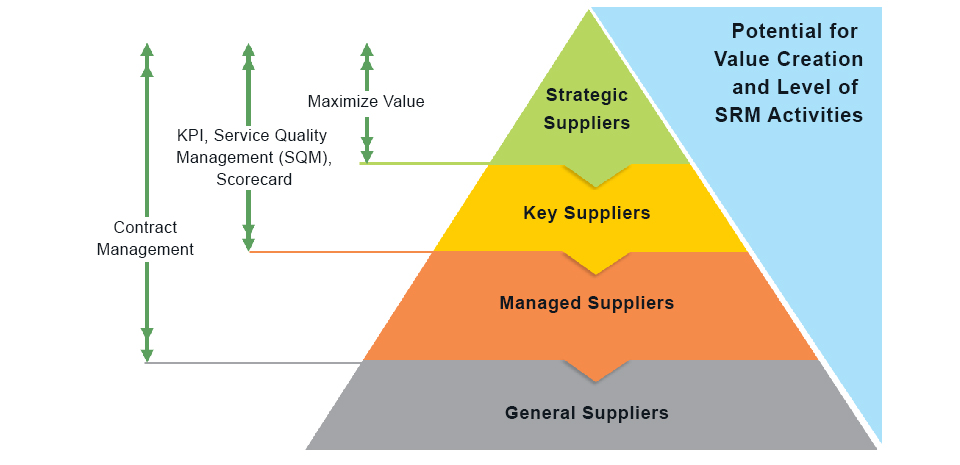
Category Management system is also the basis of Supplier Relationship Management, in terms of supplier categorization, as well as the improvement in procurement process for better alignment with product and service categories. Total procurement values from direct suppliers within Thailand and Overseas shown in Supply Chain Performance Data.)
Green Supply Chain
Green procurement is a component of Supply Chain Management. PTTEP Green Procurement Roadmap was initiated. Under PTTEP Green Procurement Roadmap (2016-2030), green procurement criteria for each function have been formulated since 2017 and appraised by the Thai Environment Institute (TEI). (Green procurement values are shown in the Supply Chain Performance Data.)
Local Content
PTTEP supports local products and services to promote the local economy. (Local refers to the country where PTTEP operates.) Particular emphasis is given to local suppliers with the capability of applying various innovations in developing goods and services accordingly to PTTEP's standards and requirements. Such development process is supported by information exchange as well as recommendations on work process improvement and safety issues, issued at meetings to follow up on suppliers' progress (Local procurement data is shown in the Supply Chain Performance Data.)
Vendor Management and Vendor Sustainable Code of Conduct
Under the commitment towards sustainable development and the development of local communities and the environment, PTTEP gives importance to supply chain management and the implementation of those rules on vendors. PTTEP Vendor Sustainable Code of Conduct was formulated, which covers relevant rules, regulations and laws. Such code is aimed at enhancing vendors' knowledge and understanding in sustainable development and ensuring that their operations integrate ethics, respect to human rights, occupational health and safety, and environmental management. PTTEP also created PTTEP Vendor Guide to identify a strategy to support, advice and educate vendors on the policy of sustainable procurement, for alignment with PTTEP Sustainable Development Policy, through various channels like pre-qualification questionnaire, bidding documents and PTTEP's website.
Quality, Transparent and Accountable Procurement
PTTEP encourages the bidding for our procurement process. This practice not only allows qualified and capable suppliers an opportunity to offer their products and services but also reduces the operating cost. Through bidding, suppliers can be controlled and evaluated against the preset standards and terms as well as the Company's policies on corruption and Safety, Security, Health and Environment (SSHE) standards. (Procurement bidding data is shown in the Supply Chain Performance Data.)
1. Key Aspects of Sustainable Procurement Process
1.1 Fair Competition
Fair competition is promoted in the procurement process, to ensure transparency and compliance with related laws, i.e. Procurement Act B.E. 2560. The process is examined for alignment with government management standards as well as the conditions specified in the Production Sharing Contract (PSC).
1.2 Supplier Selection
The supplier selection process is improved to emphasize quality and price, in order to strike contracts with qualified suppliers at an appropriate price through a transparent and accountable system. Under the PSC, PTTEP is required to submit the roadmap on annual procurement, procurement strategies and summary for Department of Mineral Fuels' approval. The roadmap serves as part of the selection process, to ensure transparency and accountability.
Assessment of Supply Chain Management Risks
1. Supplier Risk Assessment
Suppliers are one of the key stakeholders to help drive the business towards sustainability. PTTEP thus applies the following 5 steps to assess suppliers' risks to avoid and reduce ESG-related risks:
1.1 New vendor pre-qualification by screening and evaluation of vendors accordingly to product and business category
1.2 Spend analysis and risk assessment through Supply Positioning Model (SPM)
1.3 Assessment of suppliers' sustainability-related risks
1.4 Integration of sustainability aspects in selection process and contract management
1.5 Supplier risk management (Country-specific risk, Sector-specific risk, Commodity-specific risk)
Critical suppliers are Tier 1 suppliers that pose high risks in terms of business stability, expertise and supply risk. Such suppliers include those in the drilling operations and wellhead platform construction business. PTTEP selects Tier 2 suppliers by asking Tier 1 suppliers about their information (as well as information on their products and services supplied to the Company). Critical suppliers are subjected to assessment from the operations and safety function as well as annual site visits. In addition, they must devise the plans to reduce possible risks and develop an audit plan in line with PTTEP Group's operation and SSHE audit requirements, to ensure that risks are manageable and will not impact the business, local communities or the environment.
2. Supplier/Contractor Audit
PTTEP sets in place the supplier assessment desk with systematic verification of evidence and audit programs (on-site assessments) and implemented it during and after the contract period, to assess risks and ensure job completion. PTTEP also sets a plan to monitor corrections during and after the work and works with suppliers in executing corrective actions. Should economic, social and environmental risk occur, PTTEP and suppliers jointly locate the cause and find solutions. Corrective actions will then be jointly examined, taking into consideration the quality, quantity and safety in exploration and production. In consideration include the international requirements such as those of the American Petroleum Institute (API) for casing pipes and production pipes in drilling activities, the Offshore Vessel Inspection Database (OVID), the Oil Companies International Marine Forum (OCIMF), and Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) for food products; as well as minimum labor requirements, environmental laws and management standards such as ISO 14001 and ISO 45001. All vendors are informed about the Vendor Sustainable Code of Conduct and must acknowledge the code through the Vendor Management System's online form before contract signing, for their compliance and certification for the various standards in place. The assessment process also evaluates supplier production capability in order to ensure production and service quality. The process includes the assessment on suppliers' environmental, social and governance performance through an ESG On-site Audit and Key Supplier Site Visit as well as suppliers' human rights practices. The process is to ensure their compliance with PTTEP's sustainable development policy and simultaneously fosters sustainable growth for the suppliers.
The sustainability assessment criteria of PTTEP cover the sustainability performance of vendors. This is defined by a rating scale with four (4) ranges as follows: Score Range 3.26 - 4.00 means that the vendor has excellent sustainability performance. The follow-up to their sustainability performance is not required. Score Range 2.51- 3.25 means that the vendor has good sustainability performance. Only some improvements are required to increase professional performance. The follow-up to their sustainability performance is not required. Score Range 1.00 - 2.50 means that the vendor has fair sustainability performance. The vendor needs to present an ESG (ESG Corrective Action Plan) before the specified deadline. Score Range below 1.00 means that sustainability performance needs to be improved. The vendor needs to present an ESG before the next tender. Additionally, a vendor who is evaluated below 2.51 in the rating scale needs to set a corrective action plan with a deadline and list of responsible staff and submit that to the auditor. The auditor will then review the action plan to consider the possibility that it can work to get the vendor to achieve sufficient compliance with the criteria.
3. SSHE Management System for Suppliers and Contractors
PTTEP has developed the SSHE Management System (SSHE MS) for suppliers and contractors as guidance for controlling and managing their operations. The system includes the following elements:
- Integration of SSHE screening criteria to procurement procedures
- Identification and assessment of suppliers and contractors' SSHE-related risks; and specification of SSHE responsibilities, control and operational approach, and the scheduled reporting of the contractors' SSHE performance.
- Development of initiatives to improve contractors' SSHE performance, such as a performance assessment system, training on SSHE to suppliers and contractors whose tasks involve specific risks, and an SSHE suggestion system for contractors.
- Communication of SSHE expectations to suppliers and contractors through various channels in order to cultivate awareness, performance improvement and preparation to satisfy PTTEP's demands.
- Support to suppliers and contractors' SSHE performance improvement to meet PTTEP's expectations.
4. SSHE Contractor Audit
PTTEP conducted SSHE audits on contractors who were awarded high-risk jobs, accordingly to PTTEP SSHE Contractor Management Standard and Procedure. The objectives are to ensure that the contractors understand and comply with legislations and PTTEP SSHE Management System, for efficient evaluation of risk management and efficient operations.
Subjecting to the annual SSHE Contractor Audit are the jobs that pose high risks relating to security, safety, health and environment such as drilling, construction, maintenance, logistics (land, sea and air), and past performance evaluation results. New contractors are also subjected to the audit.
The process to select contractors for the audit also depends on the contractors' SSHE records. Any contractors for high-risk jobs who are very likely to cause accidents, the Company will run the audit to improve their efficiency and safety and monitor the implementation of recommended corrective actions. (SSHE Contract Audit data is shown in the Supply Chain Performance Data.)
5. Audit on Supplier Environment, Social and Governance (ESG)
PTTEP conducts an assessment on suppliers' sustainability on ESG aspect (ESG on-site audit), to assess sustainability risks in five areas: 1) corporate policy 2) business ethics 3) society 4) occupational health and safety and 5) environment, The assessment was done through a certified third party, to ensure that suppliers' ESG risks are audited and managed with the best practice. (ESG audit on contractors' data is shown in the Supply Chain Performance Data.)
Cultivation of Good Relationship with Suppliers
PTTEP have enhanced relationship with suppliers through cooperation and the improvement in supply chain management efficiency. Strategic meetings are organized under the vision of "Energy Partner of Choice", to hear their suggestions and cultivate the understanding of both sides' operations, visions and technology strategies which will improve operational efficiency and foster true cooperation. Additionally, PTTEP also cooperated with key suppliers, such as those in drilling and production site management group, to create Master Service Agreement (MSA) in advance to establish contracts standards and relevant conditions for mutual benefits and operational efficiency.
Capacity Building and Training for PTTEP Supplier and Procurement Staff
PTTEP conducts supplier training and capacity building programs to build capacity and improve ESG performance in all tier-1 suppliers which includes training for company's buyer and/or internal stakeholders on vendor ESG assessment program. The various channels were appropriately applied for Supplier's capacity building programs such as SSHE Forum, SSHE and contract commissioning kick-off meeting with contractor, on-site ESG workshop and assessment with contractor, buyer workshop and training, and contract holder certification program etc.
In PTTEP, all procurement staff can access supplier's database where ESG factors are included in vendor assessment process. Procurement staff can access those data through Vendor Management System.
For training on ESG issues relevant to procurement process, PTTEP biannually holds one day workshop to accommodate all PTTEP contract holder staff to ensure that the ESG and SSHE procurement process and requirements are met.
Logistics and Petroleum Development Support Base's Operational Strategies
The framework and strategy for logistics, as shown below, defines long-term targets in alignment with the Company's business objectives and direction. It also guides the planning on logistics operations and activities, to lead the Company towards the objectives in a sustainable manner.
PTTEP Logistics Strategy 2020 - 2024
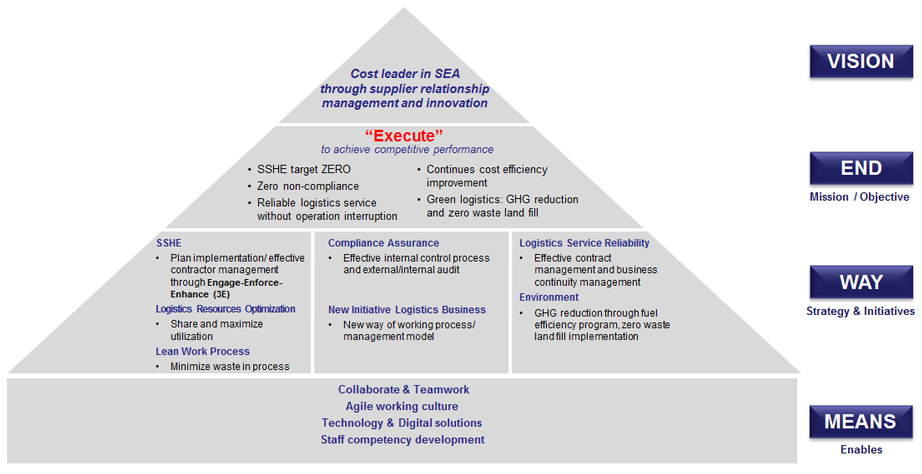
SSHE Management
PTTEP considers SSHE a key aspect in business operations and strives to become an organization without accidents through the implementation of a proactive SSHE culture. In order to instill awareness in safety and prevent serious accidents and impacts on stakeholders and the environment, PTTEP continuously organized the following activities for our contractors:
- "Safety Stand Down" was organized at all operating areas to emphasize the importance of workers and contractors' safety and to enable greater safety and maximum efficiency.
- Driver's Fatigue Detection System was implemented to monitor driver behaviors including fatigue, drowsiness, loss of concentration, and negligence. This system incorporates Facial Recognition technology and Video Analytics to monitor real-time behavior via camera installed in front of the vehicle. While in transit, the camera monitors the driver and records data. High risks will trigger a sound and vibrating signal to the driver's seat and notifies the central control room for further action. The control manager is able to assess and evaluate the driver's long-term performance through the information dashboard shown in the data analysis system, to prevent possible risks and find measures that will improve drivers' training.
- "Perfect Day" initiative was launched to incentivize personnel in assuring safety under SSHE Target Zero. The initiative is aimed at continuously enhancing safety standards and adjusting driving behavior. All drivers are urged to do their best in preventing road accidents, based on the concept that accidents are preventable. Drivers who passed assessment were rewarded.
Inventory Management
Under the policy to keep inventory at an appropriate level, PTTEP enhances inventory management efficiency, particularly for the Bongkot, Arthit and S1 projects where held high inventory volume. Key points of such actions are:
- Review inventory management to ensure the design process, features identification, procurement, storage, disbursement and amortization is efficiently implemented and aligned with the Company's internal control measures as well as relevant government regulations. In 2021, PTTEP had executed pilot project to hand pipe products, parts of Oil Country Tubular Goods (OCTG) which contain high inventory value. To utilize the pipes efficiently for maximum benefits, the Company struck consignment contracts with a supplier, having the supplier store pipes at a central storage facility in Thailand for further distribution to all PTTEP projects. Each project will place orders accordingly to what it actually needs. The approach reduces pipes in inventory and facilitates the supply of pipes. The Company also improved the pipe procurement strategies, by sourcing seamless steel pipe and removing spirals in the country. The strategy supports the development of local businesses against foreign peers, creates jobs, cuts inventory and reduces shortage risk. Another strategy concerned the reuse of OCTG thread protection, which significantly reduced plastic waste and promotes efficient resource utilization.
- Match inventory storage level with actual demands, to reduce inventory and appropriately utilize storage space. The technology based on machine learning was studied and developed, to forecast appropriate inventory levels for future demands.
- Centralize inventory management through central database, to handle unused or lightly-used and reusable items. These items are returned to the central warehouse. This reduces new orders as well as procurement process and time, which hence results in lower expenses and production cost.
- Evaluate, test and write off inventory which are degraded, obsolete or inconsistent with current operations. The process is to increase storage efficiency and reduces storage cost.
Green Logistics Management
PTTEP operates logistics according to the 3E strategy (Economics, Efficiency and Environment) and aligns the operations with Safety, Security, Health and Environment (SSHE) standards. In focus are also effective cost management, planning, forecasting, collection, international standard shipments, and reliability in the delivery process. The Company has installed the GPS vessel monitoring system in every ship since 2013 to ensure efficient use of fuel. The company controls fuel consumption and reduces green gas emissions simultaneously as well as implements the Centralized Vessel Utilization Management system.



 ...the sea has become our home and so we are conscious of our responsibilities...
...the sea has become our home and so we are conscious of our responsibilities...




 PTTEP is E&P company in Thailand, exploring for sustainable sources of petroleum for the countries we operate
PTTEP is E&P company in Thailand, exploring for sustainable sources of petroleum for the countries we operate
 SIGN IN
SIGN IN SEARCH
SEARCH




 Supply Chain Performance Data(as of 31 December 2023)
Supply Chain Performance Data(as of 31 December 2023)


